Foreseeing the Future – Current Status and Prospects of AI Applications in Machine Tools and Components
Chia-Meng Chen, Industrial Economics and Knowledge Center (IEK), ITRI
AI Empowerment, Applications First
In recent years, global political and economic instability—such as inflation, geopolitical conflicts, and regional wars—has severely impacted global market demand, posing challenges to Taiwan’s machine tool industry exports. The sharp depreciation of the Japanese yen has further intensified competitive pressure. However, as inventory reduction in the global manufacturing supply chain gradually improves in 2024, the market is returning to normal levels, and investment willingness among businesses is increasing, signaling a recovery. At the same time, the rapid rise of Artificial Intelligence (AI) is profoundly influencing various industries. As the “mother of industry,” whether machine tools can leverage this technological wave to create synergistic benefits will be a key focus in the future.
AI, or Artificial Intelligence, refers to intelligence exhibited by machines created by humans. It typically involves computer programs that simulate human thinking and behavior, and in some tasks, even surpass human capabilities. In the machine tool industry, AI offers several advantages:
- Enhancing efficiency and precision through data analysis
- Improving product quality and reducing costs via monitoring and process optimization
- Predictive diagnostics to minimize downtime and maintenance costs
The application opportunities and value can be categorized into four areas:
- Promoting Smart Manufacturing – Predict machine failures through operational data analysis, provide maintenance recommendations, and use computer vision and algorithms for automated quality inspection to ensure accuracy and consistency.
- Supporting Net-Zero Emissions – Monitor emissions data, analyze and predict environmental indicators, develop reduction strategies, and optimize material usage and processes to reduce waste and pollution.
- Enhancing Product Development and Design – Automatically generate and optimize designs based on historical data and requirements, shorten development cycles, and simulate operations to identify and resolve issues early.
- Improving Customer Service – Offer intelligent after-sales support through remote diagnostics and automated troubleshooting, and analyze feedback to understand market trends and customer preferences for customized solutions.
Global AI Applications in Machine Tools
Representative cases include:
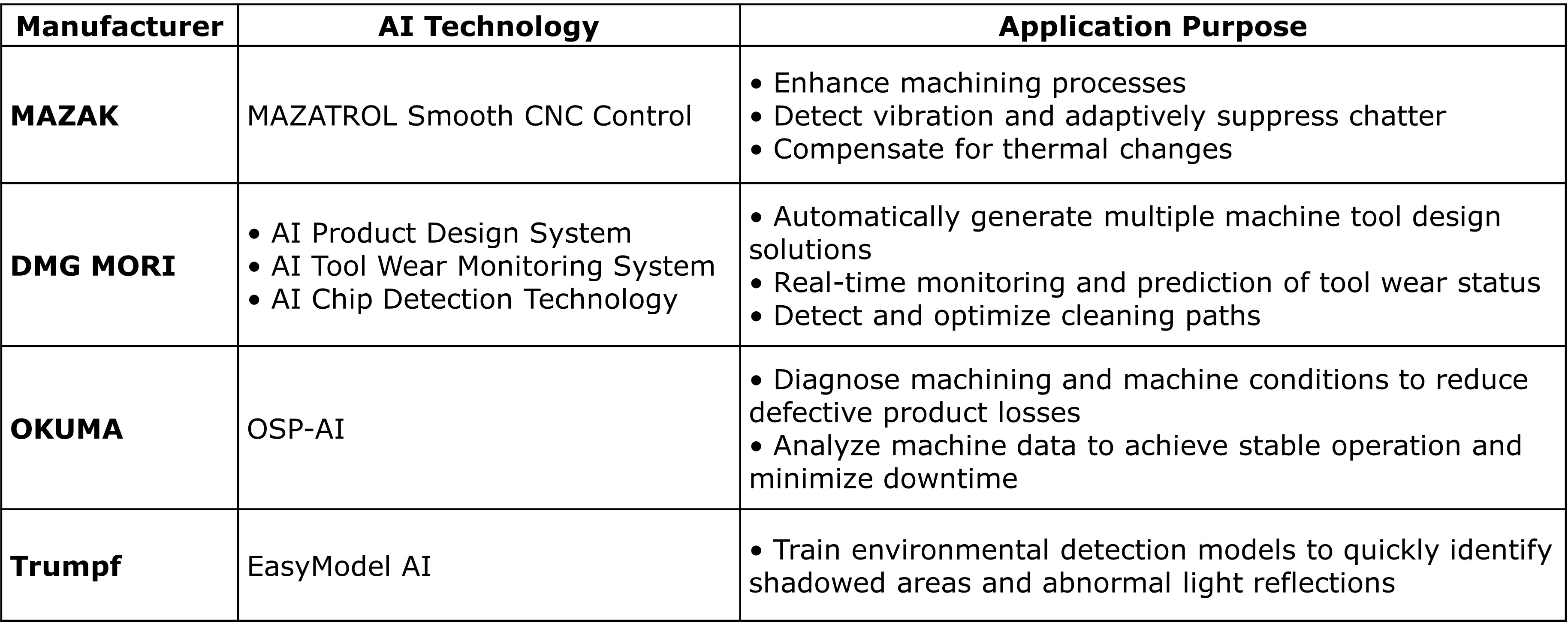
Japan – MAZAK
Introduced MAZATROL Smooth CNC Control, integrating AI with Digital Twin and automation technologies. Key features:
- Strengthening machining programs using 3D CAD data and AI
- Detecting vibration and optimizing cutting conditions via adaptive chatter control
- Compensating thermal displacement through machine learning models
- Creating digital models in the office to simulate processes, saving hardware adjustment time
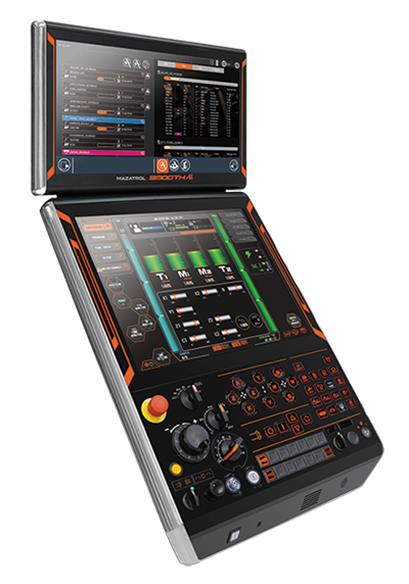 |
Source:MAZAK (2024)
Japan – DMG MORI
Developed AI-based product design systems, tool wear monitoring, and chip detection technologies. Highlights include:
- Automatic generation of multiple design solutions with performance simulation
- Real-time monitoring and prediction of tool wear
- Embedded cameras for chip detection and optimized cleaning paths
 |
Japan – OKUMA
Launched OSP-AI smart factory solutions for machine and process diagnostics, reducing defective products and downtime. Features include thermal displacement control, five-axis error compensation, and servo optimization.
 |
資料來源:OKUMA
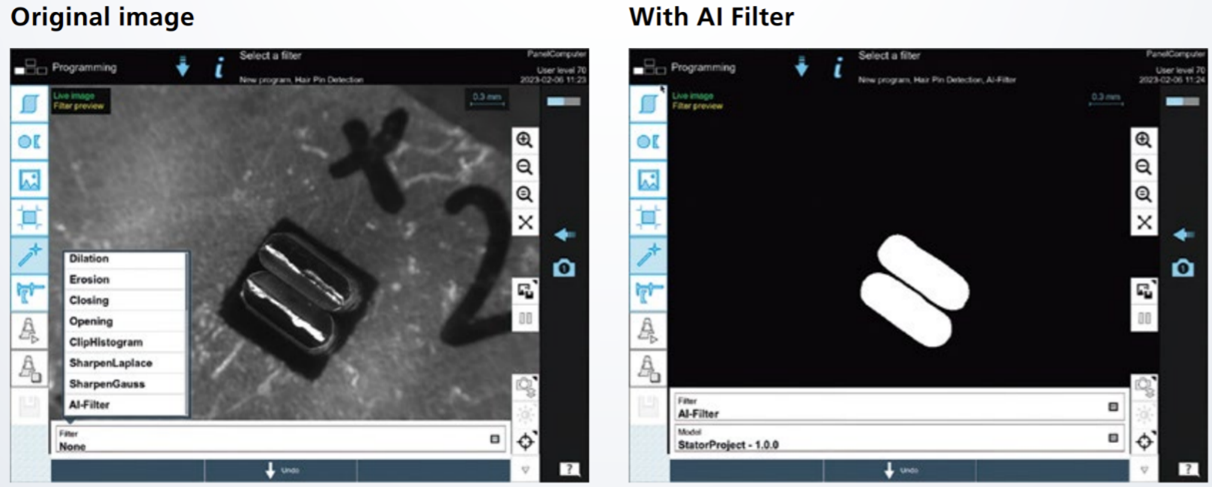
Germany – Trumpf
Uses EasyModel AI for laser processing to detect shadows, contamination, and abnormal reflections, improving cutting and welding quality.
 |
 |
Source: Industry, Science and Technology International Strategy Center (ISTI), ITRI
Domestic AI Applications in Machine Tools
Examples include:
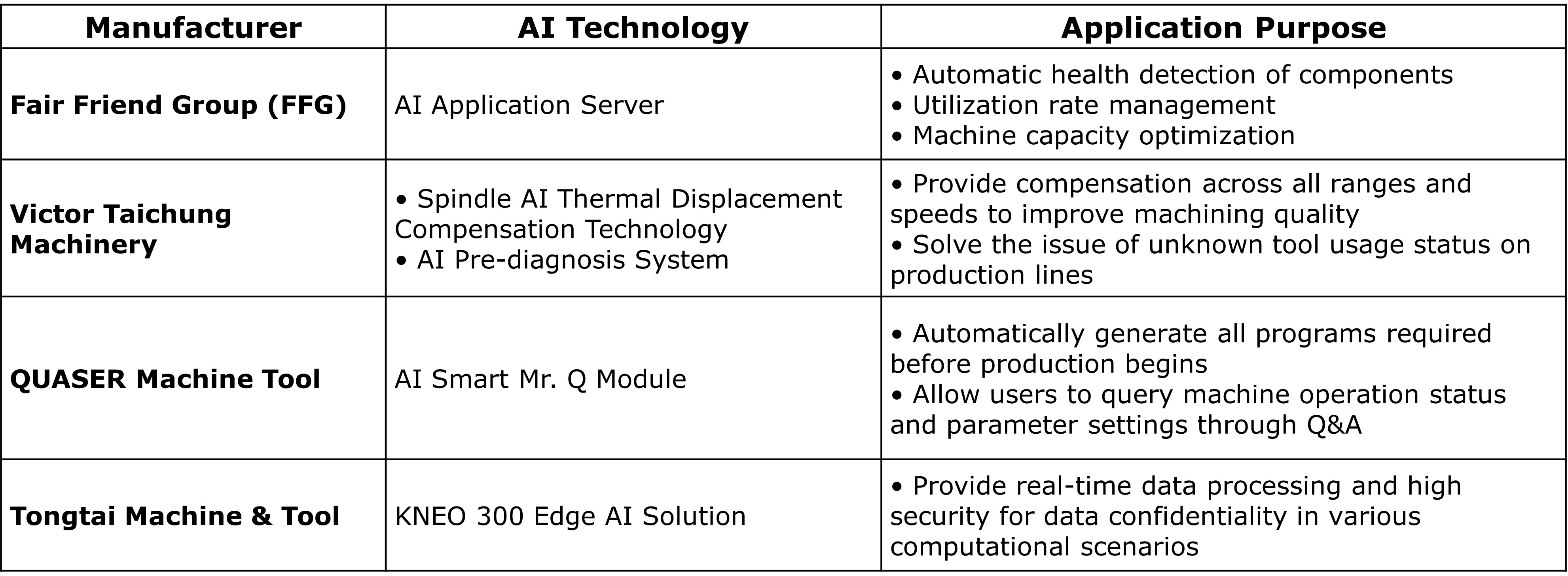
Fair Friend Group (FFG)
Implemented AI application servers for data collection, analysis, and service management. Applications include thermal compensation cards, AI-based maintenance, and vibration suppression algorithms.
|
|
Source: FFG (2024)
Vicotor Taichung Machinery
Developed spindle AI thermal compensation and predictive diagnostics for tool wear, improving machining quality and reducing defect rates.
 |
Source: Victor Taichaung Machinery (2024)
Quaser Machine Tool
Introduced Mr. Q, a generative AI module enabling conversational interaction with machines, automated warm-up processes, and real-time parameter adjustments.
 |
Source: Quaser Machine Tool (2024)
Tongtai Machine Tool
Partnered with Kneron to develop edge AI solutions for real-time data processing and secure computation in industrial manufacturing.
 |
Source: Tongtai Machine Tool (2024)
 |
Source: Industry, Science and Technology International Strategy Center (ISTI), ITRI
AI Applications in Components
Global examples:
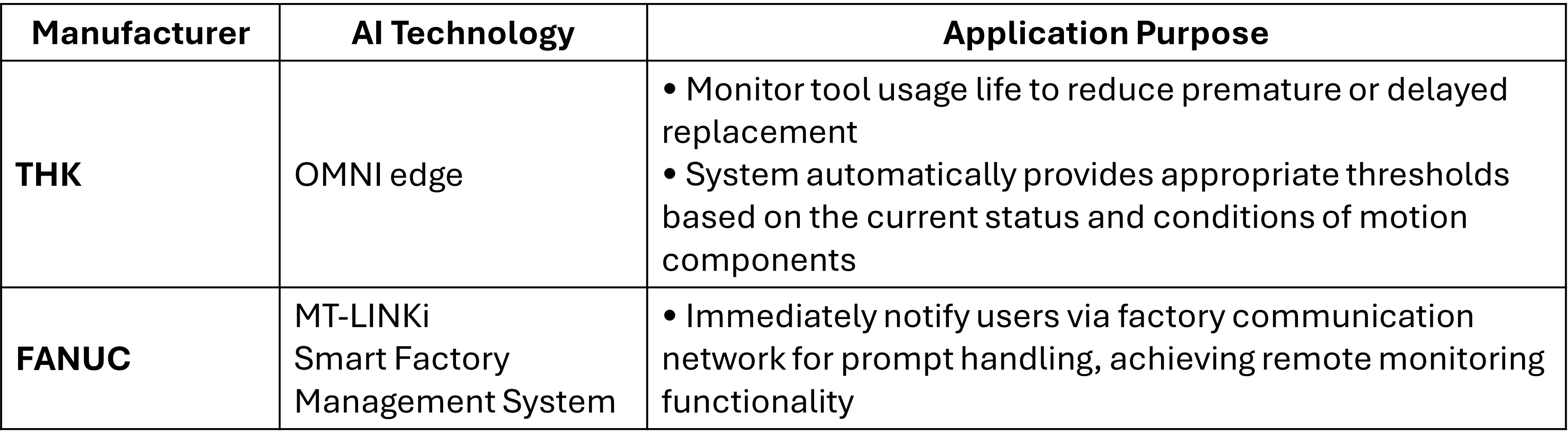
- THK – OMNI edge AI monitors tool life and linear motion components without manual threshold settings.
 |
Source: THK (2024)
- FANUC – MT-LINKi platform collects CNC machine data for remote monitoring and anomaly detection.
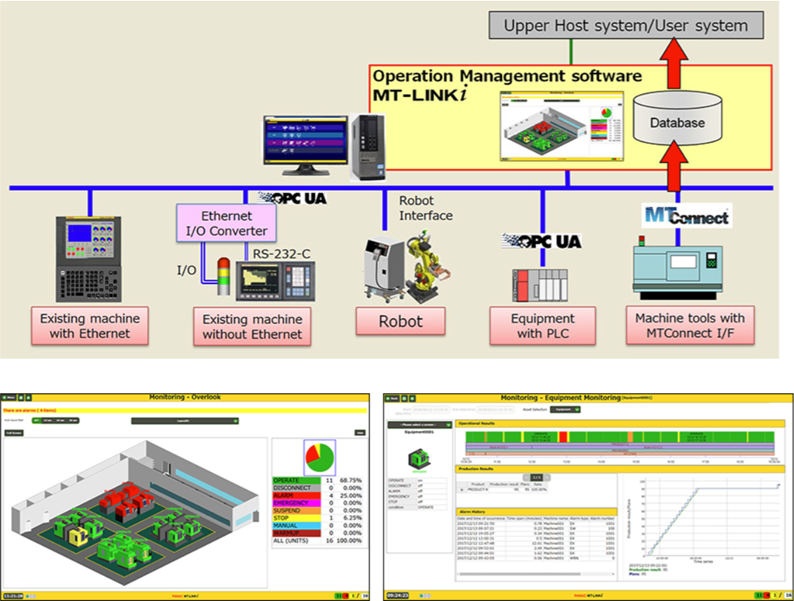 |
Source: FANUC (2024)
 |
Source: Industry, Science and Technology International Strategy Center (ISTI), ITRI
Domestic examples:
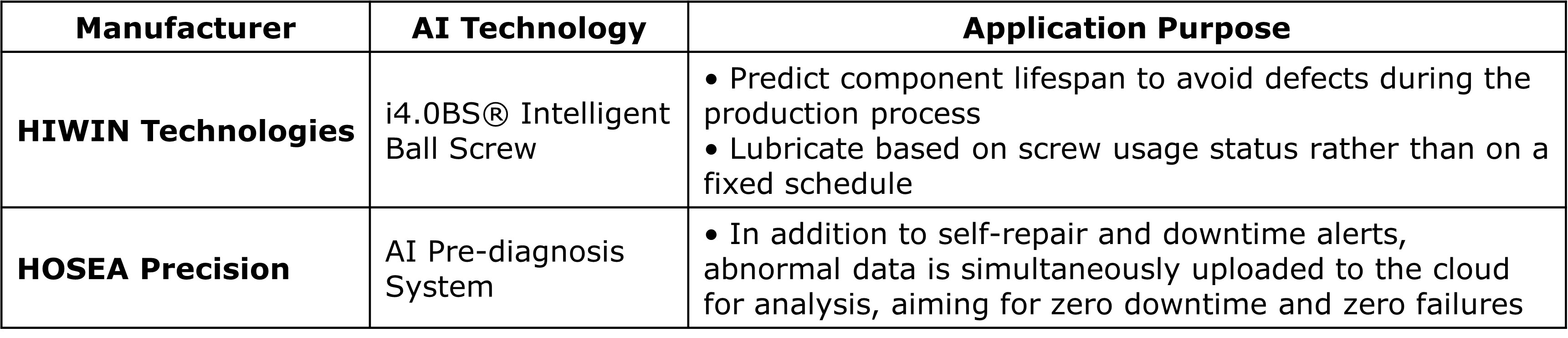
- HIWIN – Added sensors to ball screws for life prediction and optimized lubrication, reducing oil usage by 60–70%.
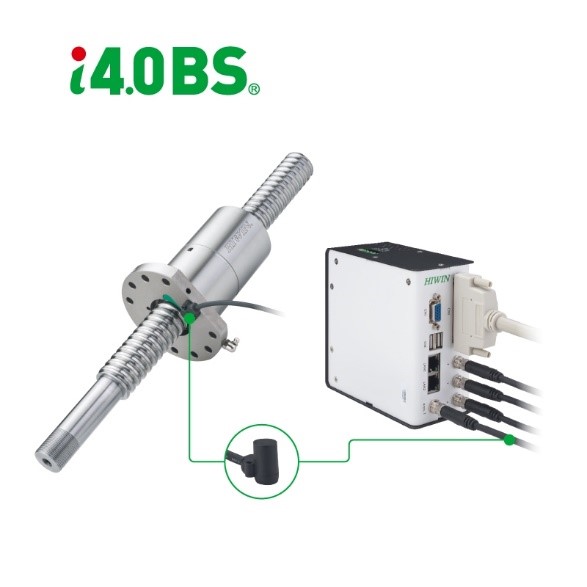 |
Souce: HIWIN (2024)
- HOSEA – Developed AI predictive diagnostics for indexing tables with cloud-based anomaly analysis, aiming for zero downtime.
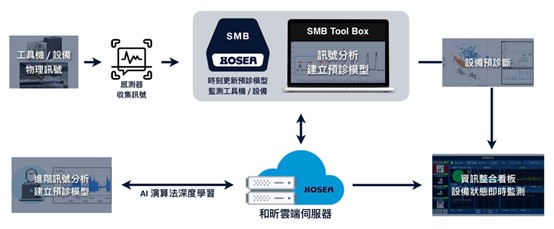 |
Source: HOSEA (2024)
 |
Source: Industry, Science and Technology International Strategy Center (ISTI), ITRI
Future Outlook and Strategic Recommendations
AI applications in machine tools and components hold immense potential, expected to revolutionize efficiency, precision, and production models.
Key trends:
- Accelerated Smart Factory Implementation – Seamless integration of machine tools with automation, robotics, and smart scheduling.
- Integration of Virtual and Physical Industrial IoT – AI and IoT enable full digital management and predictive simulations.
- Emergence of New Business Models – Transition from equipment sales to data-driven value-added services.
Recommended strategies:
- Strengthen data collection and analytics capabilities
- Collaborate deeply with AI companies and research institutions
- Develop internal AI talent
- Educate the market on AI’s benefits in cost reduction and quality improvement
AI is driving a transformative opportunity for the machine tool industry, enabling smarter production, cost reduction, and new business models. Companies should embrace this trend through collaboration and talent development to become providers of intelligent manufacturing solutions in the foreseeable future.