The Environment and Challenges of the Indian Machine Tool Market (Part Ⅱ)
Benefiting from the Indian government’s "Make in India" initiative, infrastructure investment, and the application of industrial automation and smart manufacturing technologies, the inflow of foreign capital and supply chain shifts are introducing high-end technology and management experience, further enhancing the technical level and production efficiency of local enterprises. Although the market faces challenges such as raw material price volatility, rising costs, unpredictable demand, and energy dependence, it still exhibits strong growth potential and broad development prospects. Enterprises should understand the current state of the Indian market, seize relevant opportunities, and pre-plan strategies to address the challenges.
Opportunities in the Indian Machine Tool Market
Driven by policy, market demand, and technological trends, the Indian machine tool market is projected to have significant growth opportunities in the coming years. Key driving factors will promote the development of the machine tool market, including government policies and infrastructure investment, demand for high-precision and automation technology, foreign capital inflow and supply chain shifting, and growth in domestic market and consumption. For example, the high proportional demand for machine tools from India's automotive and components, basic iron and steel, and rubber and plastics industries will directly boost the machine tool market demand.
1. Government Policies and Infrastructure Investment
-
"Make in India" Policy: Attracts domestic and foreign companies to establish manufacturing facilities in India, increasing the demand for industrial machinery and equipment. The Production Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme, launched in March 2020, initially targeted large-scale electronics manufacturing (mobile phones and components), pharmaceutical ingredients, and medical devices. In November, it expanded to 10 major industries, including automotive and components (including batteries). In 2021, drones and their components were added, encouraging 14 key industries (including electronics, pharmaceuticals, textiles, and white goods) to set up production bases in India and reduce reliance on imports from China. Furthermore, the push for localized production of electronic products like semiconductors led to the "Development of Semiconductor and Display Manufacturing Ecosystem Program" in December 2021, which allocated 760 billion rupees (about $10 billion) to promote the construction of a related industrial ecosystem. Subsidies cover four main areas: semiconductor manufacturing, display manufacturing, compound semiconductor manufacturing/packaging and testing, and semiconductor design. In 2024, a series of programs to promote the manufacturing of electric passenger cars in India were also announced.
-
Infrastructure Investment: The growth of India's heavy industry is supported by substantial investment in infrastructure, including roads, railways, and urban infrastructure. Heavy industry requires high-precision tools to manufacture large machinery, industrial equipment, and infrastructure components, thereby stimulating the demand for high-end machine tools. The adoption and promotion of advanced technologies such as AI and IoT also help improve the efficiency and productivity of machine tools in this sector. For example, the "Gati Shakti National Master Plan (NMP)," released in October 2021, brought together 16 ministries covering highways, railways, air transport, sea transport, and energy. Its goal is to provide an efficient logistics network for India's economic activities, increase industrial productivity, and connect India's transport network, including roads, railways, ports, inland waterways, coastal shipping, customs, airports, public transport, and logistics. Additionally, the National Infrastructure Pipeline (NIP) program, announced on September 17, 2022, is investing $1.4 trillion in infrastructure such as roads, railways, ports, and power, and these infrastructure projects are boosting the construction equipment and engineering machinery markets.
2. Demand for High-Precision and Automation Technology
-
Increased Demand for CNC Machine Tools: In 2024, the Indian machine tool market is dominated by CNC machine tools, which hold a market share of over 80%, while conventional machine tools account for only about 10%. As enterprises continuously pursue higher productivity and reliability, industrial automation has become an inevitable trend. Companies are gradually adopting technologies such as CNC machinery, robotics, IoT, and AI, increasing the demand for mechanical equipment and boosting the demand for CNC machine tools. The adoption of CNC machine tools allows manufacturers to increase output without adding extra labor costs and provides reliable products with fewer defects. The CNC machine tool market is expected to grow at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of $12\%$ between 2024 and 2029.
-
Increased Focus on Aerospace and Defense Industries: The allocation of the defense budget for the 2024–2025 fiscal year reflects India's strategic focus amid complex geopolitics, particularly tensions in international relations and domestic security concerns in recent years. The total budget allocation for FY 2024–2025 is $6,229.41 \text{ billion rupees}$ (about $74.3 billion), an increase of $1 \text{ billion rupees}$ (about $12 million) from FY 2022–2023, positioning India as the world's fourth largest military spender. This highlights India's emphasis on military modernization and self-reliance. The defense industry requires high-precision tools to manufacture aircraft parts, weapon systems, and other critical defense components. Therefore, the defense budget is expected to drive the high-precision machine tool market, stimulating demand for high-end machine tools.
3. Foreign Capital Inflow and Supply Chain Shifting
-
International Corporate Investment in India: Companies like Apple, Tesla, and Foxconn are expanding their investments in India, promoting the upgrading of the machinery industry. Foreign corporate investment in India will help boost demand in the local machinery market and expand the export market for Indian machinery products. Furthermore, foreign capital brings high-end technology and management experience, which helps improve the technical level and production efficiency of local Indian enterprises, enhancing product quality and service standards.
4. Domestic Market and Consumption Growth
-
Automotive Industry Expansion: The automotive industry requires high-precision tools to manufacture engine parts, transmission components, and other critical automotive components. The surge in India's auto exports further stimulates demand for machine tools. This growth is primarily driven by strong shipments of two-wheelers, passenger vehicles, and commercial vehicles.
-
Food Processing and Medical Equipment Markets: Growth in domestic demand drives increased demand for food, medical, and agricultural machinery.
Challenges in the Indian Machine Tool Market
The Indian machine tool market faces several challenges that affect its growth and development trajectory. Firstly, fluctuations and increases in raw material prices are one of the main challenges. Secondly, as manufacturing technology continually advances, it is difficult for SMEs to keep up with new technologies due to cost burden and personnel training requirements. Additionally, demand unpredictability and transportation issues also increase related costs. These challenges collectively impact the stability and growth potential of the Indian machine tool market:
1. Cost Challenges:
-
Raw Material Cost Volatility: Price fluctuations of key materials like steel, copper, and brass directly affect production costs. Due to strong demand, steel production increased in major steel-producing economies, leading to a substantial rise in steel prices over the past year. Such cost increases may force machine tool manufacturers to adjust their pricing strategies, typically passing the increased expense onto customers, which can impact demand in price-sensitive industries.
-
Maintenance and Technical Labor: Machinery requires regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance and longevity. High-end machine tools have a relatively high initial capital investment compared to traditional machine tools, which may reduce the willingness of small enterprises or those with limited budgets to adopt them. Furthermore, the repair and maintenance of machine tools require specialized technicians and equipment; the maintenance labor costs and component replacement costs for higher-end machine tools are higher, placing greater cost pressure on SMEs.
2. Unpredictable Demand and Insufficient Incentives
-
Slowdown in Global Economic Growth, coupled with the impact of global trade situations and various national trade sanctions, leads to volatility in manufacturing demand. This makes it difficult for companies to predict and plan production volumes, making cost control more challenging.
-
Lack of Highly Attractive Production Incentives from the Indian government for industries like machinery equipment affects the willingness of machinery manufacturers to set up operations.
3. Import/Export and Inter-State Transportation Issues:
-
Differences in Inter-State Taxes and Regulations: Although India has unified the GST (Goods and Services Tax), individual states may still have different tax regulations for imported machinery and equipment, such as import duties, state-level subsidies, or additional toll fees. Failure to properly handle the e-Way Bill (electronic consignment note) may lead to goods being intercepted at state borders.
-
Inter-State Transportation Permits: Some states may require additional transport permits for large or special machinery, such as an Over Dimensional Cargo Permit (ODC) for oversized equipment. Furthermore, some states have restrictions on overweight or extra-long cargo, potentially requiring special permits or changes in transportation routes.
-
Road Infrastructure, Traffic Restrictions, and Security: Road conditions in some parts of India (e.g., the Northeast, mountainous, and remote areas) are poor, which can affect the safe transport of machinery and equipment. In some remote or less secure areas, there may be a risk of theft or damage to goods.
-
Cold Chain and Special Equipment Requirements: Some precision machine tools may require temperature control or shock absorption measures, and not all logistics companies in India can provide high-specification transportation services.
-
Customs and Import Inspection: If mechanical equipment originates overseas (like Taiwan or Germany), it may face customs clearance delays upon import into India, especially when involving IS standards (Indian Standards).
-
Supply Chain Disruption Risks: Natural disasters such as large-scale farmer protests, strikes, and floods can affect transportation routes.
4. Energy Dependence:
-
Unstable Electricity Supply: Machine tools require high machining accuracy, and voltage fluctuations can affect the operation of CNC machines and even lead to equipment damage. Therefore, some regions in India (such as Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, and the Northeastern region) still face unstable electricity supply, which affects the continuous operation of machine tools.
-
High and Volatile Electricity Prices: Electricity prices vary by state; for example, Maharashtra (Mumbai) has higher electricity prices, while Tamil Nadu (Chennai) offers more favorable industrial electricity subsidies, creating differences in production costs across states. Many factories rely on diesel generators during power outages, but high diesel prices increase operating costs. In some areas (like Delhi), the government intensifies emission controls, prohibiting the use of diesel generators, which may impact backup power sources.
-
Government Push for Carbon Neutrality: India plans to achieve carbon neutrality by 2070, but the industrial sector currently relies heavily on coal-fired power generation, leading to significant pressure for carbon reduction. Moreover, some multinational corporations (such as BMW and Tesla) require their supply chains to use green energy, but Indian factories struggle to meet these requirements, potentially affecting orders.
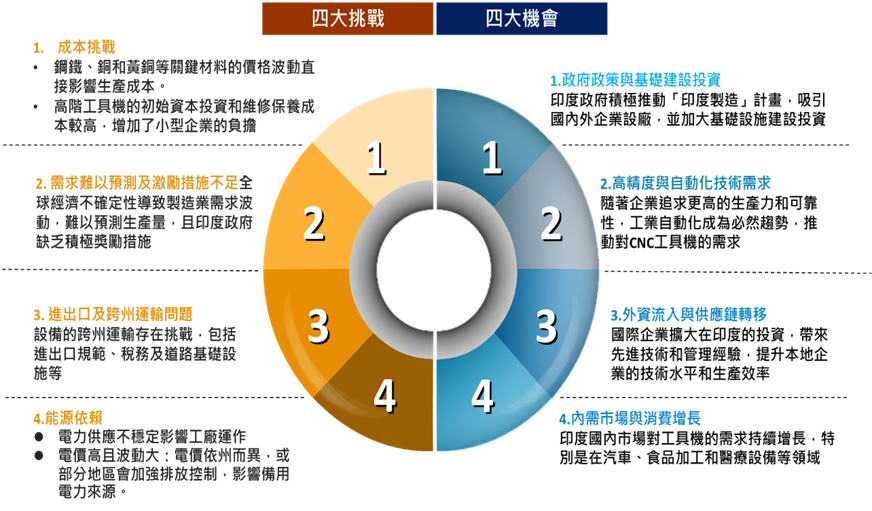
[Figure 8: Opportunities and Challenges in the Indian Machine Tool Market]
Source: IEK Consulting, ITRI (03/2025)
Conclusion
As India's manufacturing activity grows steadily, the Indian machine tool market will expand accordingly. For instance, government measures to reduce corporate taxes and strongly encourage "Make in India" have significantly increased the number of manufacturing businesses, thereby creating demand for machine tools.
Overall, the Indian machine tool market is driven by several key factors. First, the Indian government's proactive "Make in India" policy attracts domestic and foreign companies to set up facilities in India, increasing the demand for industrial machinery and equipment. These policies include the PLI scheme and the Semiconductor and Display Manufacturing Ecosystem Program, aimed at promoting the development of the electronic manufacturing and electric vehicle industries. Second, industries such as India's automotive and components, basic iron and steel, and rubber and plastics account for a high proportion of machine tool demand, and their growth will directly drive the machine tool market demand.
Furthermore, the inflow of foreign capital and supply chain shifts are crucial factors promoting the growth of the Indian machine tool market. The expansion of international corporate investment in India helps enhance the technical level and production efficiency of local Indian enterprises. At the same time, the growth of India's domestic market and consumption will also boost the development of the machine tool market, particularly in the automotive, food processing, and medical equipment sectors.
However, the Indian machine tool market also faces several challenges, such as the difficulty in managing volatile raw material prices and other costs, electricity price fluctuations and power instability, market demand uncertainty, and land/sea transportation issues. Overall, the Indian machine tool market is expected to achieve stable growth in the coming years but needs to overcome these challenges to fully realize its potential.





