Global Machine Tool Market Trends and Risk-Opportunity Analysis in 2024
Machine Tool Market Still Holds Growth Potential
According to Fortune Business Insights, the global machine tool market is expected to continue growing, driven by the increasing adoption of robotics to enhance automation and human-machine interaction. The rapid expansion of smart factories, fueled by real-time connectivity needs, is a prominent trend. For example, IoT-enabled machine tools that provide real-time data insights and process optimization are a key focus for industry players. In August 2020, Hurco launched a new series of CNC turning centers—TM12Mi XP, TM10Mi XP, and TM8Mi XP—featuring tool turrets equipped with powered tools. The rise of additive manufacturing is also expected to boost future market growth, as manufacturers seek faster and more cost-effective production processes. Additionally, growing demand for advanced machining solutions in aerospace and automotive industries presents significant opportunities, as these sectors increasingly adopt precision engineering and efficient processes, driving demand for high-end machine tools.
International Relations as Market Variables
Geopolitical factors have begun reshaping the machine tool industry, particularly regarding whether certain nations support military and nuclear development. For instance, despite EU sanctions prohibiting equipment and technology exports to Russia, DMG MORI—one of the world’s largest cutting machine tool manufacturers—continued supporting Russia’s military industry through its Ulyanovsk plant established in 2015. This factory, serving Rostec and other state-owned entities producing missiles and aircraft engines for SU, MiG, and Il fighter/bomber jets, was critical because Russia lacked sufficient modern machine tools. After the Russia-Ukraine war erupted on March 14, 2022, DMG MORI announced its withdrawal and closure of the Ulyanovsk plant. However, corporate records show DMG MORI RUS LLC and Ulyanovsk Machine Tool Plant LLC continued operations with unchanged ownership. Despite a 50% revenue drop in 2022, both entities retained 92 employees and reportedly assembled at least 200 machines using pre-existing parts. Post-March 2022, Russian entities sourced parts and machines via Asia. ImportGenius data reveals Ulyanovsk received $261,000 worth of parts from India, while DMG MORI RUS purchased $195,000 worth of machines from a Chinese supplier. DMG MORI now sells indirectly through affiliates, actively supplying sanctioned Russian military firms—a practice likely to face future restrictions.
China’s Machine Tool Industry: Current Status and Outlook
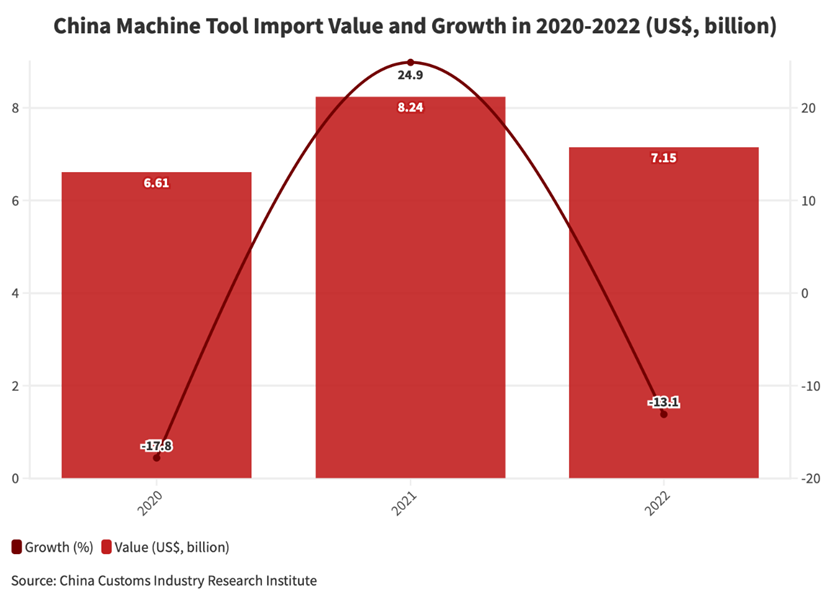
China’s machine tool industry has surged, competing in Southeast Asia and other developing markets. With a market value exceeding RMB 200 billion (approx. $27.86 billion), China ranks first globally. Under 20 leading firms drive adoption of advanced technologies, prioritizing precision and smart CNC tools and components. Despite strong government support, China remains heavily reliant on imported high-end CNC tools and parts, sustaining foreign supplier demand. Major domestic players include Shenyang Machine Tool Co., Dalian Machine Tool Group, Qiqihar No.2 Machine Tool Group, Nanjing No.1 Machine Tool Plant, and Jinan No.1 Machine Tool Co.
China accounts for 32% of global machine tool consumption, reflecting robust machining demand aligned with manufacturing expansion. In 2020, metal-cutting machine tool output surged to 446,000 units (+5.9% YoY), while metal-forming tools fell to 202,000 units (-8.6%). Production rebounded in 2021 post-pandemic but weakened in 2022 amid global economic shifts: 572,000 metal-cutting units and 183,000 metal-forming units. China’s reliance on imported high-end tools underscores the importance of trade as a competitiveness indicator. Notably, domestic mid-to-high-end CNC tools have a localization rate below 10%. In 2021, China’s average export price was $300 per unit, versus $76,700 for imports. Automotive dominates low-end CNC applications (40%), followed by aerospace (17%), molds (13%), and construction machinery (10%). In 2022, China exported 20.87 million machines (-26.4% YoY), yet machine tool exports rose 10.3% to $9.5 billion, with average unit price climbing to $500.
Future growth will be driven by EV demand and sustainability policies. China’s automotive sector continues expanding, with EV and autonomous vehicle investments boosting high-end CNC tool demand. Leading automakers like BYD and NIO invest in advanced CNC-integrated facilities for efficiency and quality. Automation and 3D printing integration with CNC tools define China’s industrial trajectory. Manufacturers aim to increase CNC adoption to streamline operations and minimize errors. Huawei and DJI exemplify firms investing in advanced CNC technologies to transform manufacturing capabilities. CNC integration in power generation is also rising, with State Grid and China Huaneng deploying CNC tools to enhance automation and meet energy-saving goals.
|
|
Source:China Customs Industry Research Institute
Risk Management Imperatives for 2024
Chief Risk Officers (CROs) report to boards and CEOs on insurance, IT security, audits, compliance, fraud prevention, and global business risks. CROs design processes to prevent losses from procedural or system failures, ensuring disaster recovery, business continuity, and regulatory compliance. Key risk categories include:
- Compliance Risk: Meeting legal and regulatory obligations.
- Operational Risk: Business disruptions, labor issues, technology failures, supplier loss.
- Reputational Risk: Damage to organizational standing among stakeholders.
- Strategic Risk: Threats to executing corporate strategy.
Traditionally, CRO roles focused on operational, financial, and regulatory risks. Recently, new risks—geopolitical, cybersecurity, environmental, supply chain shifts, and digital technology—have emerged, defying historical analysis. Oliver Wyman reports CROs spent ~50% of 2023 on non-financial risks, mainly compliance and resilience, with the remainder split between financial (30%) and strategic (20%) risks. KPMG highlights key CRO priorities:
- De-risking: Top concerns include regulatory compliance (28% poorly prepared), recession (40%), and geopolitical risk (37%).
- Growth & Strategy Alignment: 82% of CROs report strong executive support; future focus includes emerging risk analysis, strategy alignment, and predictive modeling.
- Regulatory Pressure: Compliance challenges expected to dominate next 2–5 years, with regulators (33%) and investors (22%) exerting greatest pressure.
- Tools & Technology: 88% of firms plan ≥5% budget increases for risk management. AI and ML rank as top enablers, followed by cloud and network solutions. Three-quarters of firms already use AI/ML in risk processes, alongside data visualization and targeted training.
In today’s volatile economy, robust risk assessment is critical. Firms must strengthen both “hard” components (analytics engines, data infrastructure) and “soft” components (skills development). Technology plays a vital role: unified compliance platforms centralize policies; LMS tools deliver training; analytics identify patterns and anomalies; risk assessment software automates evaluations; compliance systems track regulatory changes; incident management tools log and resolve issues; secure communication platforms enable real-time coordination; and e-learning enhances risk awareness.
DTCC’s survey shows 81% of respondents rank geopolitical risk as the top threat for 2024 (up from 68% in 2023), marking its second consecutive year as the leading concern. Inflation ranks second (55%), down from 61% last year, as demand and economic activity soften. Geopolitical tensions and conflicts drive persistent uncertainty, while inflation remains a significant challenge shaping the risk landscape.