Development of Immersive Interactive Remote Collaborative Engineering Environment for Smart Factories
The impact of the pandemic and changes in geopolitical dynamics have prompted the manufacturing industry to reorganize production bases and supply chains. During this restructuring process, quickly resolving various anomalies in processes, equipment, and production lines across different locations has become a major challenge. The trend of Industry 4.0, combined with issues such as 5G/6G communication, AI, and carbon emission restrictions, has attracted even greater attention from manufacturers. Among these, leveraging immersive interaction for remote production line technology projection has emerged as a new market opportunity. This article outlines ITRI’s recent efforts to integrate immersive interaction technology into smart factories for remote collaborative engineering applications and proposes potential future business models.
Overview of the Immersive Interaction Industry
Post-pandemic, the acceptance of remote meetings has significantly increased. The need for supply chain reorganization and relocation of manufacturing bases has driven manufacturers and equipment suppliers to strengthen remote collaborative engineering technologies to reduce labor and travel costs associated with technical services. Taiwan’s New Southbound Policy encourages Taiwanese businesses to establish new factories or upgrade production lines in Southeast Asia. To address shortages of high-level technical personnel and reduce the cost of remote technical projection, the demand for remote collaborative engineering technology has further increased.
Technologies such as Virtual Reality (VR), Augmented Reality (AR), and Mixed Reality (MR) have long been explored for remote collaboration. However, due to limitations in semiconductor, optical, and communication component technologies, related hardware and software were expensive and offered poor user experiences. In recent years, advancements in these technologies, combined with cost reductions, cloud computing, and AI, have enabled immersive interaction to gain significant traction in commercial entertainment and e-sports. Yet, applying these technologies to industrial scenarios still faces challenges—primarily how to convert industrial IoT data and engineering computation results into interactive 3D components and enable human interaction. While numerous computational modules have been developed during years of smart manufacturing and smart machinery research, projecting these results into 3D environments remains underdeveloped.
Smart Manufacturing Trends
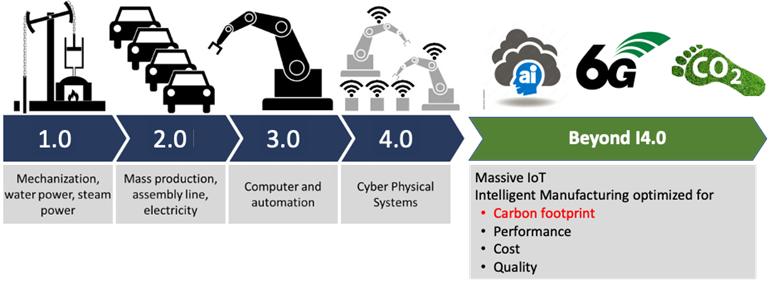
Since the concept of Industry 4.0 was introduced, countries worldwide have emphasized the importance of manufacturing and actively promoted smart manufacturing development. This concept has revolutionized the industry, shifting from traditional centralized production to more flexible, intelligent, and networked manufacturing. This transformation not only impacts manufacturing itself but also profoundly reshapes the global economic landscape.
One key driver is the rapid advancement of Artificial Intelligence (AI). As AI technology evolves, its applications in smart manufacturing continue to expand. Meanwhile, the maturity of cloud computing business models enables manufacturing services to migrate to the cloud, allowing companies to leverage remote resources and data for more efficient production and management.
Another critical technology is 5G communication. Its high speed and low latency make it ideal for industrial IoT, enhancing data storage, analysis, and application performance. This also facilitates the concept of digital twins—deep connections between physical equipment and their virtual models—enabling better monitoring, optimization, and prediction of manufacturing processes.
 |
Source:complied by Smart Machinery Technology Center, ITRI (2024)
Additionally, the global push for net-zero carbon emissions is driving innovation in smart manufacturing. Manufacturers must now consider energy efficiency and carbon emissions alongside product performance and quality. Low-carbon smart manufacturing has become a priority, requiring cleaner energy and optimized processes to reduce emissions while considering the entire product lifecycle.
Labor shortages due to aging populations further necessitate automation and smart technologies to boost productivity. High-level technical talent is increasingly scarce, making remote collaborative engineering a vital tool for global cooperation and knowledge sharing.
According to forecasts, the smart manufacturing market will reach $620 billion by 2026, driven by automation, remote collaboration, VR, equipment diagnostics, and process simulation deployed via cloud platforms.
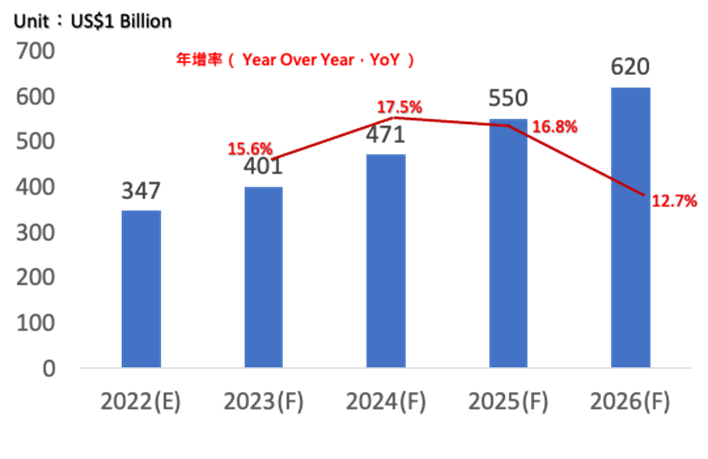 |
Source:TrendForce, complied by Smart Machinery Technology Center of ITRI (2024)
From Engineering Computation to Interactive Environments
Despite the rise of smart manufacturing, projecting engineering analysis software and data visualization charts into immersive virtual environments faces technical hurdles:
- Projection Issues: Existing engineering software is designed for office or lab use, not interactive virtual environments.
- File Format Conversion: Output formats from engineering software are rarely compatible with multimedia or gaming tools, requiring complex conversions.
- Static Geometry: Current geometric data is static, limiting interactivity in virtual environments.
- Collaborative Editing: Enabling dynamic, real-time, multi-user editing requires a suitable geometric data format.
To address these challenges, we propose using Universal Scene Description (USD)—a format developed by Pixar and adopted by NVIDIA for its Omniverse platform. USD supports dynamic descriptions, composition, simulation, and collaboration in 3D scenes, making it ideal for engineering and virtual manufacturing environments.
Advantages of USD
- Multi-Software Support: Adopted by NVIDIA, Apple, Adobe, and others, with conversion interfaces for various 3D modeling tools.
- Dynamic, Real-Time Collaboration: Supports multi-user editing, enabling on-the-fly changes to virtual scenes, including charts, annotations, and remote equipment operations.
- Data Integrity: Prevents issues like broken surfaces or geometric discontinuities during format conversion.
- Cost Savings: Broad adoption reduces development costs for remote collaboration services and digital content.
For industries like machine tools and mechanical manufacturing, USD enables seamless integration of analysis results into interactive virtual environments, fostering real-time collaboration and decision-making.
Current Development and Future Plans
Multi-dimensional collaboration offers cross-disciplinary insights for analyzing production anomalies but increases meeting complexity. Without proper workflows, scene definitions, and information exchange mechanisms, meetings risk becoming unfocused. Many process issues involve coupled physical phenomena, making it difficult for a single expert to resolve them remotely. Immersive collaborative meetings that bring together process engineers, equipment specialists, and control experts—supported by IoT data, production history, and simulation—can accelerate problem-solving.
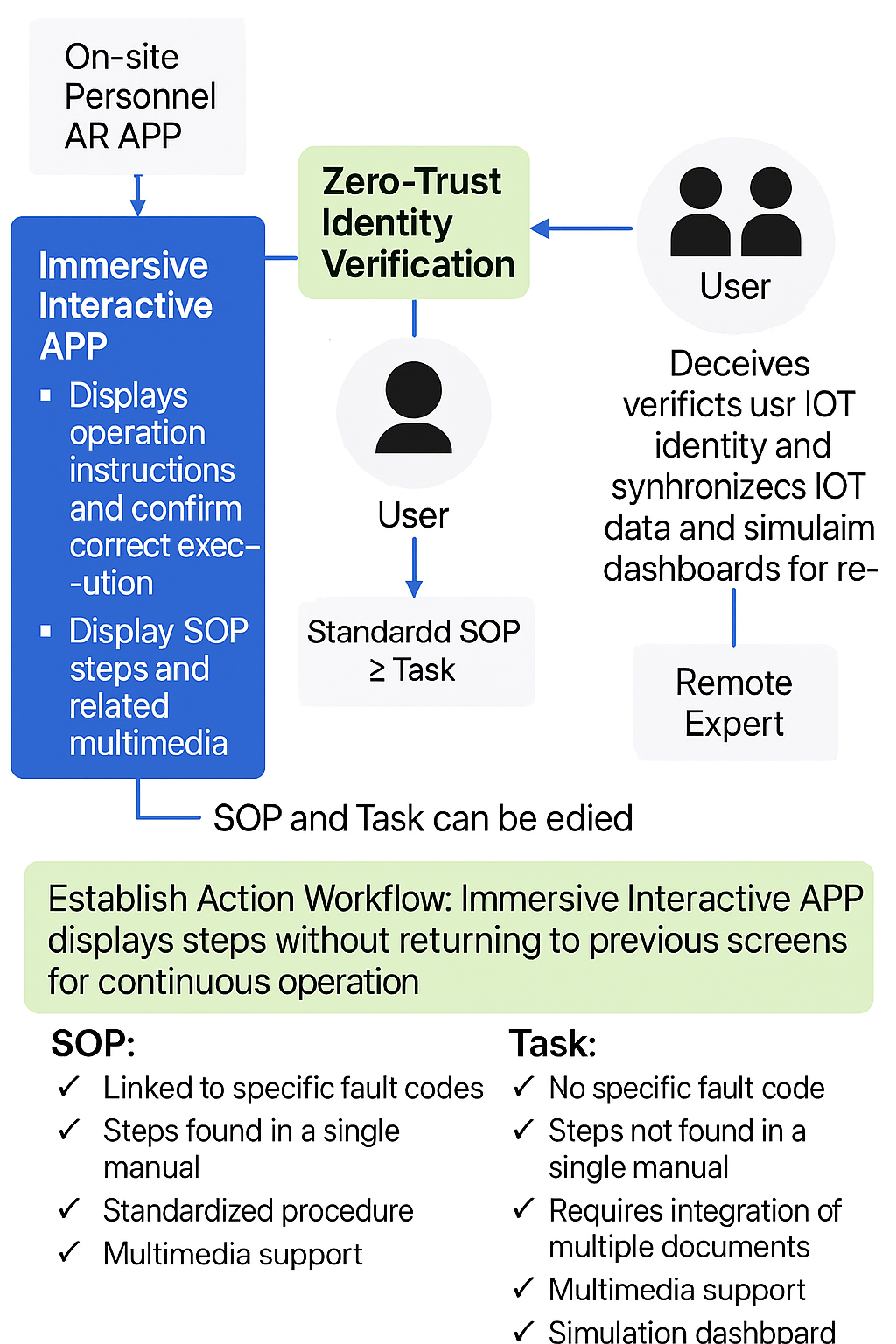
Tasks for anomaly resolution fall into two categories:
- Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs): Linked to specific fault codes with predefined steps.
- Custom Tasks: Require integrating information from multiple sources to define steps.
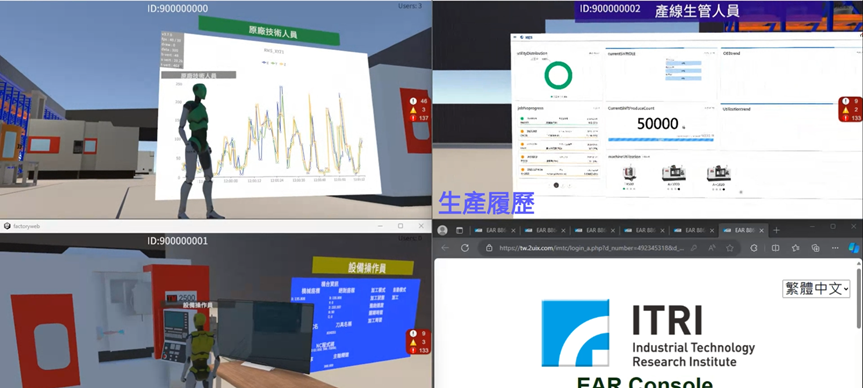 |
Source:Smart Machinery Technology Center, ITRI (2024)
ITRI has developed a task editor allowing experts to define steps with text, multimedia, and simulation dashboards. These task files can be imported into immersive environments for synchronized viewing by on-site personnel and remote experts, ensuring accurate execution and real-time monitoring.
 |
Source:Smart Machinery Technology Center, ITRI (2024)
| Figure 5. Robot adjustment after battery replacement. | Figure 6. Annotating operational steps corresponding to machine positions in an immersive 3D interactive scene. | Figure 7. Remote experts synchronously monitoring on-site workflows and operational steps. |
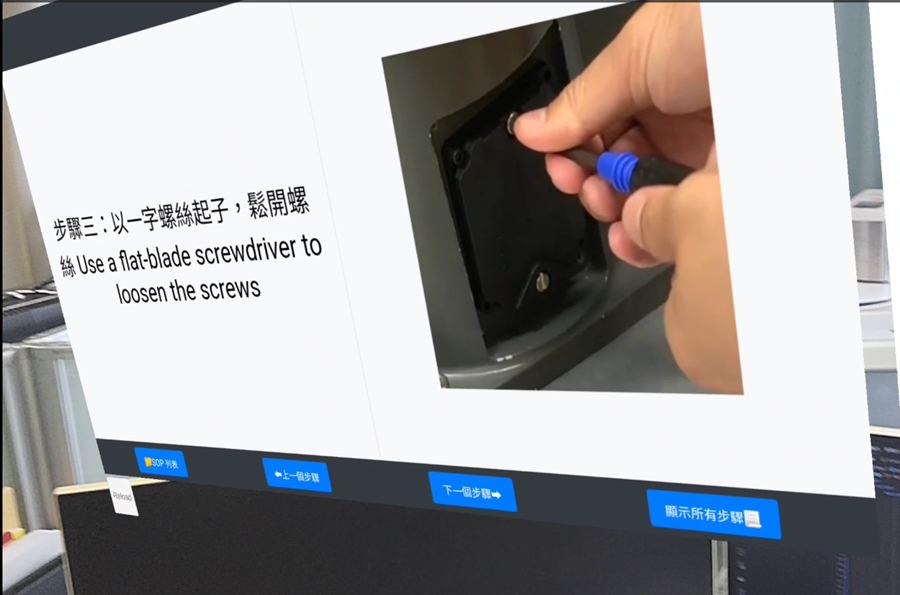 |
 |
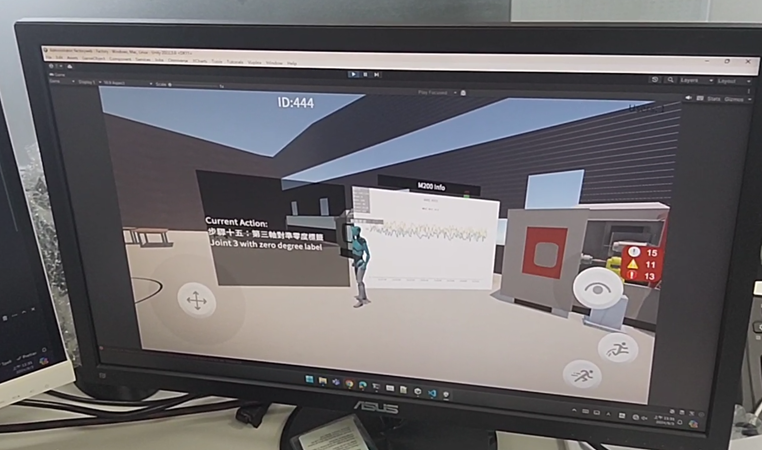 |
Source:Smart Machinery Technology Center, ITRI (2024)
For example, in a robot battery replacement scenario, the immersive environment displays step-by-step instructions and 3D indicators of machine positions, enabling remote experts to verify correctness via synchronized IoT data.
Conclusion
Immersive interactive remote collaborative engineering services will be a key driver of smart manufacturing. By overcoming the limitations of traditional remote meeting systems and enabling higher-dimensional collaboration, these technologies can shorten anomaly resolution times for overseas production lines, accelerating digital transformation and enhancing competitiveness.
ITRI will continue developing immersive interaction applications for various manufacturing scenarios, validating them in smart manufacturing testbeds to support domestic manufacturers in meeting global challenges such as net-zero carbon emissions and labor shortages.
Reference
- Lee, J., Bagheri, B., & Kao, H. A. (2015). A Cyber-Physical Systems architecture for Industry 4.0-based manufacturing systems. Manufacturing Letters, 3, 18-23.
- Schuh, G., Potente, T., & Uhlmann, E. (2017). Digital Twin in Manufacturing: A Categorical Literature Review and Classification. Procedia CIRP, 61, 141-146.
- Vasiu, R., & Filip, F. G. (2016). Cloud Manufacturing as a Solution for SMEs in the Context of Industry 4.0. Procedia CIRP, 52, 135-140.
- Shi, Y., Luo, J., & Wang, X. (2020). A survey of cyber-physical systems. Future Generation Computer Systems, 105, 525-542.
- Statista Research Department. (2021). Global smart manufacturing market size 2019-2026. Retrieved from https
- Pixar Animation Studios. (n.d.). Universal Scene Description. https://graphics.pixar.com/usd/docs/index.html
- 2. NVIDIA. (n.d.). NVIDIA Omniverse. https://developer.nvidia.com/nvidia-omniverse-platform
- 3. Apple. (n.d.). USD (Universal Scene Description). https://developer.apple.com/usd/
- Adobe. (n.d.). USD Integration for Adobe Substance 3D Designer. https://www.adobe.com/products/substance3d-designer.html





