2025 Machine Tool Industry Development Trends - Supply Chain Regionalization & Deeper Digital Applications & Diversified End Users
In 2024, the global economy continued to face challenges from geopolitics, regional wars, and financial turmoil, leaving the machine tool industry in an uneasy environment. Furthermore, factors such as government controls on exports to Russia and Turkey, the yen's depreciation exceeding that of the New Taiwan Dollar, and the gradual unfolding of the effects of China's Ministry of Commerce suspending the ECFA early harvest list contributed to a third consecutive year of decline in both export and production value, further complicating the industry's future development.
The ongoing Russo-Ukrainian and Middle Eastern wars have extended their reach, impacting energy and other related markets in neighboring regions. Japan's ultra-loose monetary policy has led to a depreciation of the yen, weakening Taiwan's export competitiveness. Overall, the machine tool industry's performance in 2024 remains hampered by global geopolitical conflicts, the yen's depreciation, and the slow recovery of consumption in mainland China, Taiwan's largest export market for machine tools. Domestic demand remains weak, resulting in a nearly 20% decrease in output value (Figure 1). Looking ahead to 2025, while the US and China face headwinds in consumption and investment respectively, other major economies such as Europe and Japan are expected to recover. Emerging markets and developing economies in Southeast Asia, South Asia, Africa, and Latin America are also projected to outperform 2024. Therefore, most major international forecasting agencies believe that global economic growth in 2025 will be similar to that of 2024, with global trade growth expected to be higher than in 2024, which will benefit Taiwan's export performance. In the machine tool industry, due to the lower base in 2024, there is an opportunity for output value growth in 2025.
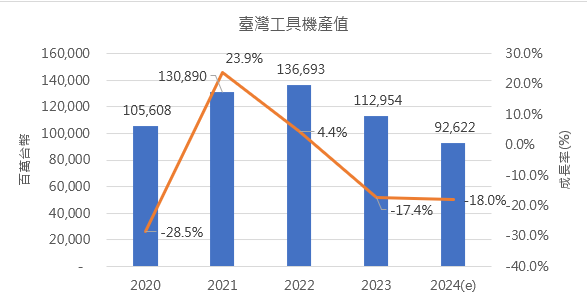
Figure 1. Output Value and Annual Growth Rate of Taiwan's Machine Tool Industry.
Recently, Taiwan's machine tool industry has ventured into new industrial fields such as semiconductor equipment, which were previously unexplored.The economic conditions of major export destinations such as Europe, America, and Asia are also impacting export performance. In today's rapidly changing environment, only through global strategic adjustments, technological innovation, and value chain extension can the industry have a chance to drive the next wave of development. After a tumultuous 2024, the industry hopes for a turnaround in 2025. With inflationary pressures easing, market interest rates falling, boosting corporate investment, elections in major global countries concluding, and regional political situations becoming more stable, the overall machine tool industry is expected to bottom out and rebound in 2025, with the industry's prosperity gradually increasing quarter by quarter.
Regionalization of supply chain & deepening of digital application & diversification of end users have become the development trend of the machine tool industry.
In 2024, it will still be a challenging year. Geopolitics, regional wars, financial turmoil and other factors will affect the overall global economy. In order to cope with the impact of the macro environment and revitalize the machine tool industry in Taiwan Province, in March 2024, Taiwan Province Machine Tool and Parts Industry Association (TMBA) entrusted the Obstetrics International Institute of ITRI to carry out the research case of “Taiwan Province Machine Tool Competitiveness Change and Strategy Suggestion”.
This study mainly analyzed the future development direction of Taiwan Province machine tools and parts and the reasons for the change in competitiveness in recent years. It proposed strategic practices to strengthen the overall competitiveness of the industry, explored the key factors influencing competitiveness, and formulated corresponding development directions and international layout strategies.
The specific research projects included: analysis of changes in competitiveness of Taiwan Province machine tools; financial report analysis of listed manufacturers; development models and trends of manufacturers in Chinese mainland; investigation of substitution of machine tools imported from Chinese mainland; analysis of operating models of machine tool factories in Germany and the United States; and inventory of competitors of Taiwan Province manufacturers.
According to the report, Chinese mainland became the second largest machine tool importer in Taiwan Province mainly due to the combined effects of price competitiveness, quality and technology, domestic market demand and international trade policies.
To address this situation, questionnaire surveys and expert interviews suggested that enterprises need to strengthen product differentiation and added value, improve quality and technical capability, and closely monitor international market changes and trade policy developments to enhance competitiveness under import substitution.
Regarding overseas production deployment, establishing production bases in Chinese mainland or other countries can improve production efficiency and meet local market demand. However, it also brings industrial impact, competitive pressure, and structural changes to local economies and the global machine tool market.
Competitor analysis showed that Japanese and South Korean manufacturers are the main competitors of Taiwan Province machine tool manufacturers, regardless of enterprise size. In the component sector, Japanese manufacturers are the primary competitors for both large and small-to-medium enterprises.
Survey results also revealed that enterprises are most concerned about talent acquisition and competitive pressure from South Korea, Chinese mainland and India, as well as solutions such as technology upgrading, product structure adjustment and government support. These topics are recommended as key directions for further research.
In addition, topics worthy of further discussion include: investigation of major and emerging markets as marketing channels, evaluation of overseas factory investments, enhancement of industry added value, and analysis of terminal industry applications, especially opportunities for mid- to high-end machine tools.
In terms of competitiveness promotion strategies, the report proposed several key directions:
– Improving product quality and stability through standardization, component universality and Total Quality Management (TQM).
– Accelerating expansion into emerging application markets such as semiconductor equipment, aerospace and new energy.
– Strengthening manufacturers’ competitive resources through alliances and group integration.
– Enhancing international operational layout focusing on Southeast Asia with stronger marketing, service, warehousing and flexible overseas production.
With the publication of this report, it was emphasized that the machine tool industry in Taiwan Province should focus on integrating quality, technology and resources, and strengthen internationalization to find a sustainable growth path in a highly competitive global market.
Based on the research findings and current industrial observations, it is predicted that supply chain regionalization, deepening digital application and diversification of end users will be the main development trends of the machine tool industry.
Under the influence of geopolitics and trade policies, with Trump re-elected as President of the United States, the U.S. is expected to strengthen its “Made in America” policy and promote supply chain reshoring to North America. This will force Taiwan Province machine tool manufacturers to re-evaluate supply chain layouts and adapt quickly to regionalized demand. Tightened tariffs and trade restrictions may also increase cross-border costs, pushing companies to expand into Southeast Asia and India.
With the deepening of digital applications, AI and digital twin technologies are expected to significantly improve machine tool efficiency, accuracy, predictive maintenance capabilities, and product development speed. Competitiveness will gradually shift from hardware performance to digital capabilities, with data analytics and remote operation and maintenance becoming important profit sources.
In terms of end-user diversification, emerging markets such as semiconductor equipment, unmanned aerial vehicles and robotics are growing rapidly. These industries require high-precision, highly customized and highly automated solutions, providing Taiwan Province manufacturers with opportunities to move away from pure price competition.
In the face of global political and economic volatility, Taiwan Province enterprises must continuously monitor changes and remain flexible. U.S.–China trade tensions, export restrictions and pressures to shift production to the U.S. may force companies to rebalance management costs and intellectual property risks.
Meanwhile, digital technologies such as AI, 5G and digital twins can promote both DX (digital transformation) and GX (green transformation). Accelerating digitalization and low-carbon development is regarded as the main solution for future industrial upgrading.
In recent years, the Industrial Technology Department of the Ministry of Economic Affairs has invested resources to help develop high-end machine tool technologies, successfully introducing them into domestic manufacturers and enabling entry into supply chains of AIRBUS and Tesla, strengthening Taiwan Province’s global industrial position.
Semiconductor equipment, robotics and drones are considered the most important future application opportunities. Successful entry into the semiconductor supply chain would significantly enhance technical capabilities, market scale, added value, international influence and industrial upgrading.
Despite opportunities, Taiwan Province manufacturers face strong pressure from improving Chinese mainland products and price-advantaged Japanese products. To break through, it is critical to actively develop new application fields and strengthen high-end capabilities.
In November 2024, the Japanese International Machine Tool Exhibition (JIMTOF 2024) was held, with more than 60 Taiwan Province manufacturers participating. The scale of the exhibition nearly doubled compared to the previous event, rekindling optimism in the industry. However, behind this optimism, supplier data showed that overall orders were reduced by about half, and most leading companies experienced declining revenues.
The industry faces three long-term structural problems:
-
Insufficient economies of scale and excessive fragmentation.
-
Weak competitiveness, unable to outperform China on price or Japan on quality.
-
Lack of transformation momentum, with difficulties in green machine tools, semiconductor entry and mergers and acquisitions.
Although green machine tools are strategically important, short-term market demand remains weak and carbon reduction effects are difficult to quantify. Entry into the semiconductor industry requires long-term technological accumulation and cannot generate quick returns. Mergers and acquisitions are being promoted, but management capability and competitiveness remain the core success factors.
In conclusion, opportunities and risks coexist in the Taiwan Province machine tool industry. Short-term demand driven by geopolitical factors cannot sustain long-term growth. To move forward, the industry must focus on three major directions:
– Long-term deployment of green machine tools.
– Deepening technology capabilities and entering high-end sectors such as semiconductors.
– Promoting mergers, acquisitions and alliance integration to enhance global competitiveness.
Taiwan Province’s machine tool industry stands at a critical crossroads. Only by strengthening core competitiveness and deepening strategic transformation can it escape short-term volatility and achieve sustainable long-term development.





